Barriers to learning from experience
Why do accidents tend to recur?
Overview
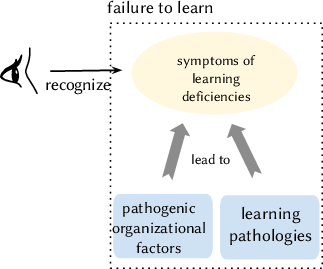
Operational experience feedback and learning from unwanted events, incidents and accidents are important sources of progress in safety management. A number of obstacles tend to decrease the effectiveness of learning from experience. We describe some symptoms of failure to learn, such as under-reporting and fixation on immediate causes, then describe underlying pathogenic organizational factors that can be responsible for the symptoms of ineffective learning.
Several steps are required to achieve learning:
- reporting
- analysis
- planning corrective actions
- implementing corrective actions (including information sharing)
- monitoring their effectiveness
Obstacles (technical, organizational or related to the organizational culture) may appear within each step, and learning is not effective unless every step is completed.
From an operational standpoint, these slides aim to help practitioners to identify opportunities for improving their event learning process. They should be useful in the context of a process review of your organization’s learning system.
Course material
 |
Barriers to learning from experience |
The symptoms of ineffective organizational learning discussed in the slides, that can be observed by an informed observer or auditor who examines a company’s learning system, are:
- Under-reporting
- Analyses stop at immediate causes
- Self-centeredness
- Ineffective followup on recommendations
- No evaluation of effectiveness of actions
- Lack of feedback to operators’ mental models of system safety
- Loss of knowledge/expertise (amnesia)
- Bad news are not welcome
- Ritualization of experience feedback procedures
These symptoms reflect a number of pathogenic organizational conditions that hinder effective learning:
- Denial
- Complacency
- Resistance to change
- Inappropriate organizational beliefs
- Overconfidence in the investigation team’s capabilities
- Anxiety or fear
- Corporate dilemma between learning and fear of liability
- Lack of psychological safety
- Self-censorship
- Cultural lack of experience of criticism
- Drift into failure
- Inadequate communication
- Conflicting messages
- Pursuit of the wrong kind of excellence
Other resources
We recommend the following sources of further information on this topic:
UK HSE report A survey of processes and systems for learning lessons from incidents within HSE and industry, UK Health and Safety Executive, 2005
ESReDA documents on Dynamic learning as the followup from safety investigations
UK Chartered Institute of Ergonomics and Human Factors (CIEHF) report Learning from Adverse Events
RoSPA advice on learning from safety failure
Oxford Research Encyclopedia entry Collective Knowledge for Industrial Disaster Prevention
Published:
Last updated: