Decisions on risk treatment
Overview
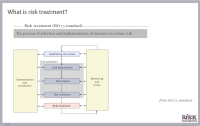
 Risk
treatment is the process of selecting and implementing measures to
reduce risk. Methods include risk avoidance, risk modification (reducing
the probability of the unwanted event or mitigating its consequences)
and risk transfer (hedging and insurance). An organization’s decisions
on which levels of risk are acceptable, and how to allocate investments
between risk reduction and risk transfer, depend on the organization’s
risk attitude.
Risk
treatment is the process of selecting and implementing measures to
reduce risk. Methods include risk avoidance, risk modification (reducing
the probability of the unwanted event or mitigating its consequences)
and risk transfer (hedging and insurance). An organization’s decisions
on which levels of risk are acceptable, and how to allocate investments
between risk reduction and risk transfer, depend on the organization’s
risk attitude.
Decision-making concerning risk and safety management is often affected by a tension between two partially compatible bodies of knowledge:
the engineering view of objective risk assessment, decision trees and rational decision-making
the social sciences view of risk as a socially constructed phenomenon, of risk-related decisions as the result of a satisficing (“good enough”) process in which political considerations may weigh more than risk metrics
This submodule, using concepts from economics and psychology, covers topics including
risk attitudes, risk perception and their impact on decision-making
utility and risk aversion
insurance, liability law and regulation as social methods of risk control
This submodule is a part of the risk management module.
Learning objectives
Upon completion of this submodule, you should be able to:
Understand risk attitude, risk appetite and perceptions of risk
Understand different forms of risk transfer, including hedging and insurance
Course material
 |
Risk treatment: introduction |
 |
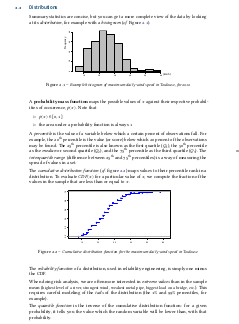
Economic viewpoint on risk transfer |
 |
Handout on risk treatment |
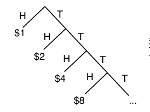 |
Python notebook on the Saint Petersburg paradox |
Other resources
We recommend the following sources of further information on this topic:
Materials for the Principles of microeconomics course at MIT, via MIT OpenCourseWare
Material for the Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management course at Sloan School of Management (via MIT OpenCourseWare)
Published:
Last updated:
